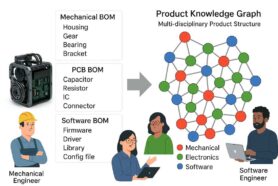
OpenBOM is built on a forward-thinking strategy centered around data-first principles, a flexible data model, a product knowledge graph, and seamless integration. At its core, OpenBOM enables manufacturing companies to organize product information and manage its lifecycle with precision and flexibility.
The foundation of OpenBOM’s approach is the Digital Bill of Materials (Digital BOM), a data modeling concept that helps companies handle product data by leveraging modern graph-based data management technologies.
In this article, we’ll explore five important characteristics of the Digital BOM and how it sets OpenBOM apart from traditional PLM systems.
Data Objects
The foundation of OpenBOM’s data model is the Data Object. A Data Object in OpenBOM is a flexible, virtual table where every element of product information is represented with an Item ID and associated properties. Here is an example of a data object type in OpenBOM (e.g. catalog).
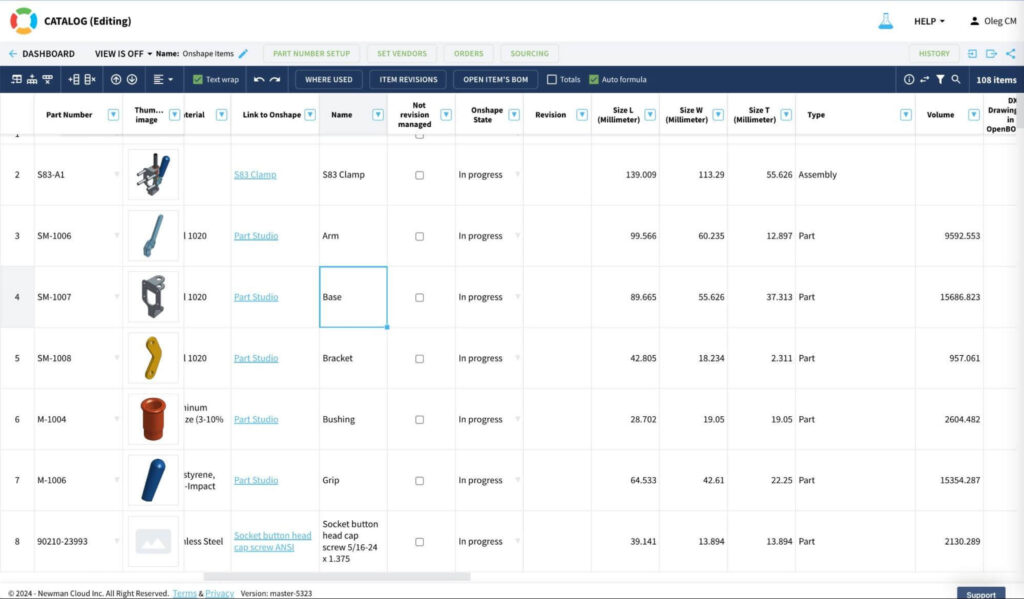
This flexible structure allows users to define and manage properties that suit their specific needs. Whether it’s material type, dimensions, or vendor information, OpenBOM accommodates a wide range of property types.
By allowing users to model their data dynamically, OpenBOM ensures that the Digital BOM evolves with your business needs.
Item Catalogs and the Reference-Instance Model
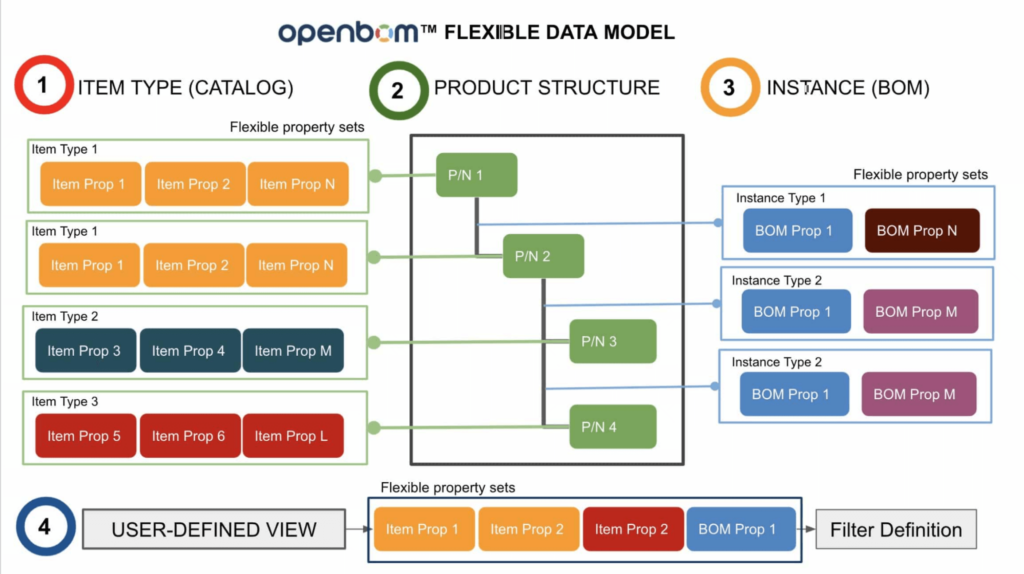
At the core of OpenBOM’s product modeling capabilities is the concept of Item Catalogs and the Reference-Instance Model.
- Item Catalogs: These are flexible collections of data objects that represent different types of product information, such as materials, standard parts, fasteners, electrical components, and assemblies. The classification is entirely customizable, enabling businesses to organize data their way.
- Reference-Instance Model: This innovative mechanism connects catalog items (references) to specific BOM entries (instances). It allows you to instantiate components and seamlessly represent them across different product structures.
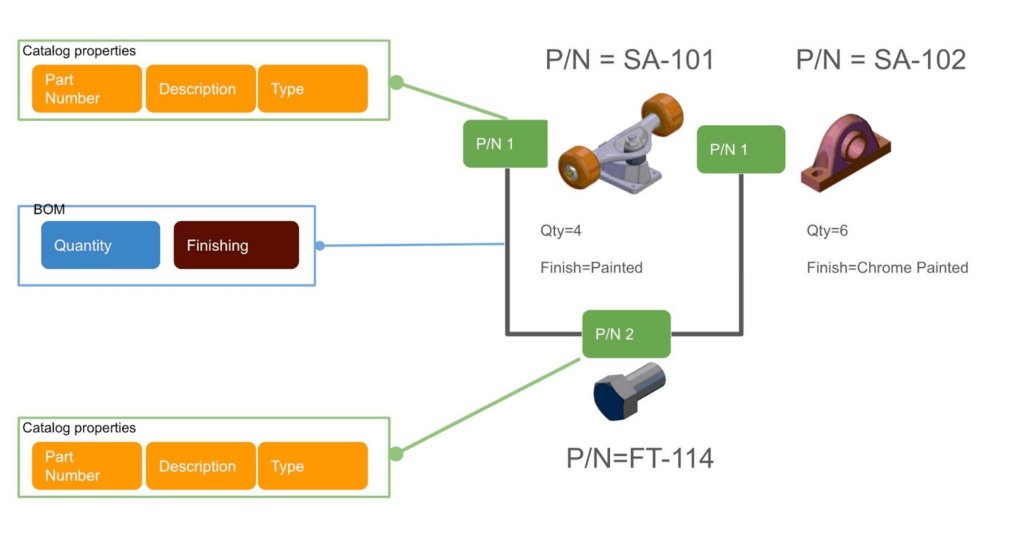
For example, a bolt defined in a catalog can be referenced multiple times in different assemblies, ensuring consistency and traceability.
The following picture shows the overall product reference instance model
xBOM
OpenBOM’s xBOM model is a game-changer in managing complex product structures with an unparalleled level of flexibility and configuration.
The xBOM model allows you to organize and manage multiple BOM types for the same product, enabling tailored representations for various business needs.
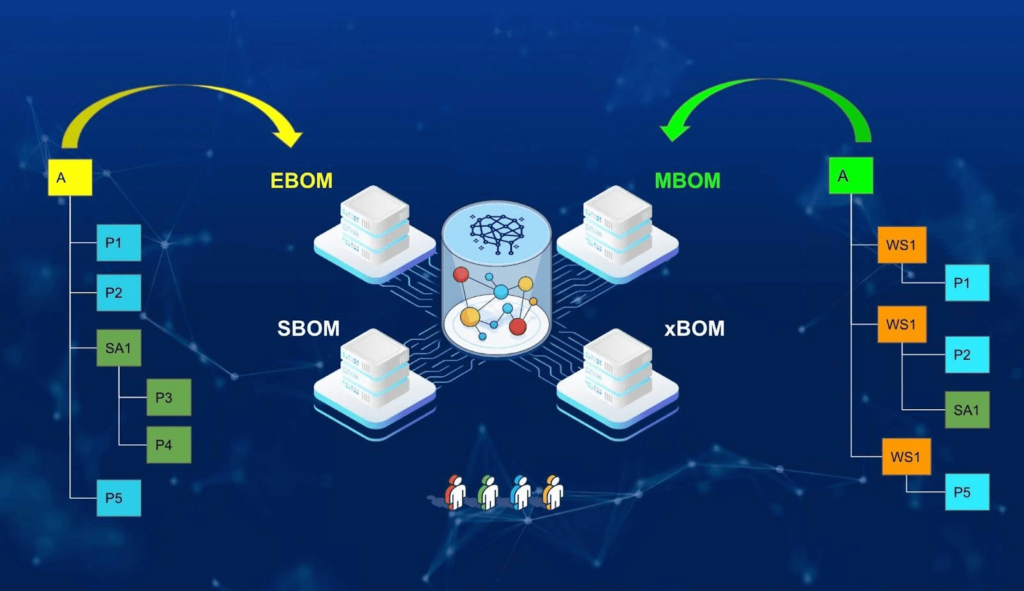
With xBOM, you can create:
- Engineering BOM (EBOM): Focused on design and engineering details.
- Manufacturing BOM (MBOM): Structured for production processes.
- Service BOM (SBOM): Tailored for maintenance and repair operations.
- Any other BOM types…
This multi-view BOM architecture ensures that your teams work with the most relevant data while maintaining a single source of truth across multiple lifecycle stages.
Here is an example of a BOM presentation in a multi-level table form.
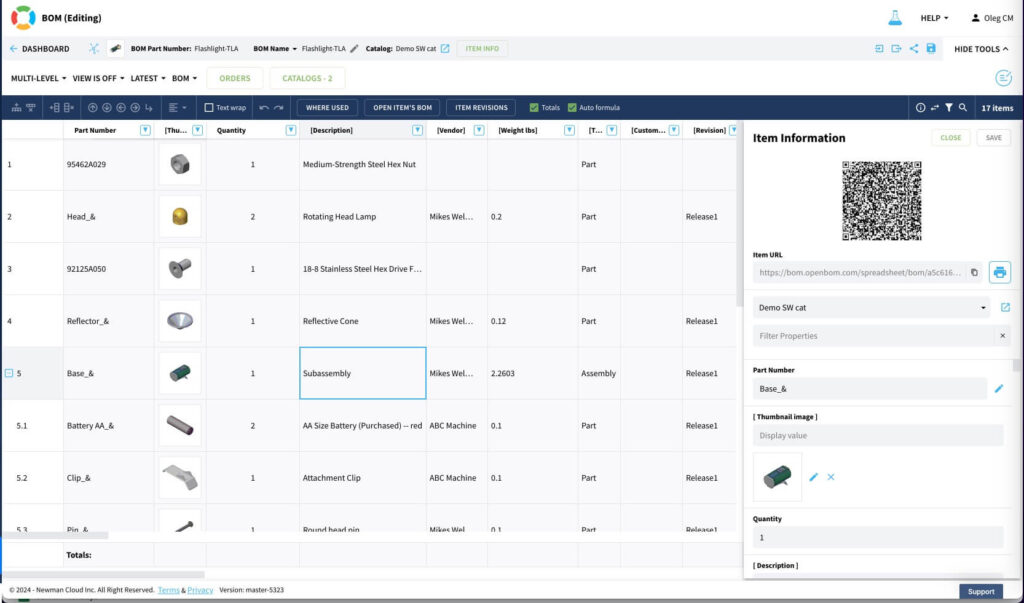
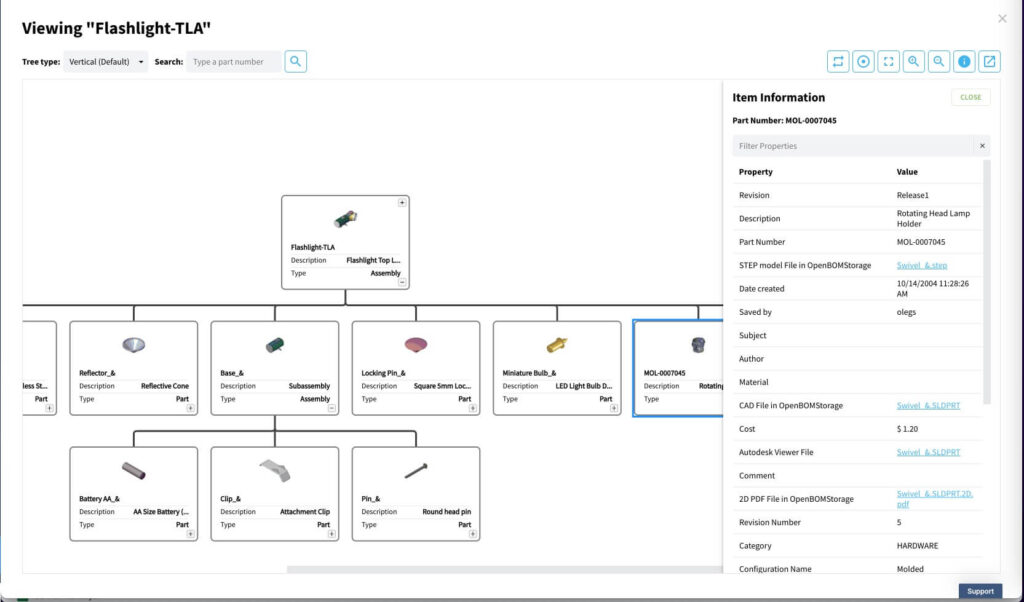
The same BOM is presented as a hierarchical tree with relationships.
Item/BOM Lifecycle
Managing product data effectively requires robust lifecycle management. OpenBOM’s Item and BOM Lifecycle features ensure complete control over revisions and states.
Key capabilities include:
- Creating revisions of items and BOMs with a “latest state” and an unlimited number of revisions.
- Connecting revisions using the reference-instance model, ensuring that part revisions are seamlessly linked to corresponding assembly revisions.
This approach delivers traceability and ensures that every stakeholder accesses accurate and up-to-date product information.
Design Objects and Item Lifecycle
Beyond managing product structures, OpenBOM handles design files and CAD information with dedicated lifecycle management.
- Design Objects: These are records for CAD files and other design assets, enabling companies to manage associated data effectively.
- Version Management: OpenBOM supports unlimited design versions, ensuring that engineers and designers can track changes and maintain design history independently of the item lifecycle.
This separation between item and design lifecycles provides unparalleled flexibility for managing both product and design data.
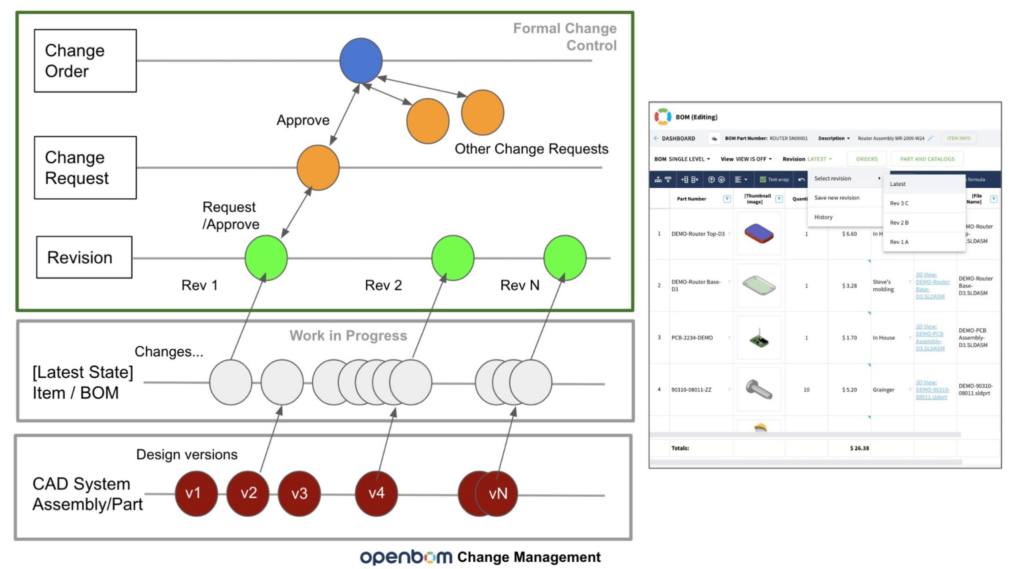
Product Lifecycle Overall Picture
In this diagram, you can see all elements of the OpenBOM product lifecycle – Design Item (File) Versions, Latest Workspace, Revisions, and Change Approval Mechanism.
A User-Centric Experience
OpenBOM’s user experience is designed to be visual, intuitive, and interactive. Key features include:
- Visual Management: Navigate and manage objects in a graphical interface.
- Slice and Dice: Analyze and reorganize information dynamically.
- xBOM Navigation: Effortlessly move between different BOM structures and design items.
Check out this demo video to see how OpenBOM delivers a seamless user experience for managing Digital BOMs.
Conclusion
OpenBOM’s unique data model combines mechanical, electronic, and software elements into a single, data-driven system. This system, powered by a product knowledge graph, allows businesses to manage their product data with unparalleled flexibility and efficiency.
By leveraging graph database technology and knowledge graph principles, OpenBOM ensures robust data management for modern manufacturing needs.
Want to learn more about OpenBOM’s Digital BOM?
REGISTER FOR FREE today and experience the future of product data management.Best,
Oleg
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.