In the modern landscape of design and manufacturing, efficient data management is a critical element. The increasing complexity of product designs and the proliferation of data sources necessitate a robust system that can unify and streamline information. What was before a model in MCAD system, nowadays is a system collected from multiple design data sources – mechanical, electronics, and software. The complexity is skyrocketing, but the data management systems used by engineering and manufacturing companies are largely unchanged from the 1990s.
At OpenBOM, our vision is to change the paradigm of data management by bringing modern tools and concepts that the industry is consolidating from building large global web platforms, as well as from the ability to consolidate and manage large amounts of information.
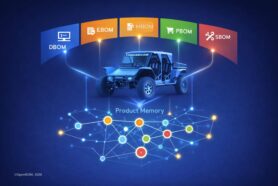
Product knowledge graph platform technology is a foundation of data management in OpenBOM and addresses the challenge of complexity by constructing a comprehensive knowledge graph through the integration of diverse design data into a single, cohesive representation.
In this article, I will share some ideas on how OpenBOM does it and also would like to speak about the opportunity of developing AI based on knowledge graph and data representation as well as what impact it might have on the industry.
Understanding the Knowledge Graph Concept
A knowledge graph is a structured representation of information where entities (such as parts, assemblies, and documents) are interconnected by relationships. This graph-based approach allows for the visualization and analysis of complex data relationships, enabling more intelligent data retrieval and insights. In the context of design and manufacturing, a knowledge graph can encapsulate information about product designs, materials, suppliers, and engineering changes, among others.
If you never heard about knowledge graphs before, this is a time to catch up. You can start here – Knowledge Graphs on Wikipedia. You can also check more information about it on our blog –why OpenBOM is using Graph Database and OpenBOM Knowledge Graph vision and roadmap.
The OpenBOM Approach to Data Integration
In this article, I want to touch on a specific aspect of OpenBOM knowledge graph building from multiple design data sources. The foundation of OpenBOM design data integration is building multiple add-ins and connectors that can bring data from each design data source to OpenBOM. This allows OpenBOM to build a design digital thread.
The importance of this approach and a thing that OpenBOM excels in is to create a unified knowledge graph by collecting and synthesizing data from multiple CAD data sources. Here’s how it achieves this:
Data Aggregation from Multiple CAD Systems: OpenBOM integrates seamlessly with various CAD (Computer-Aided Design) systems such as SolidWorks, Autodesk, and PTC. This integration ensures that data from different design environments are brought into a single platform without the need for manual data entry, reducing errors and saving time.
Real-Time Collaboration and Updates: The platform enables real-time collaboration among team members, ensuring that any updates or changes to the design data are instantly reflected across the knowledge graph. This feature fosters a collaborative environment where all stakeholders have access to the most current information.
Centralized Engineering Bill of Materials (BOM) Management: OpenBOM consolidates Bill of Materials from different sources into a single, unified representation. This centralization allows for easier tracking of parts and assemblies, ensuring consistency and accuracy in the design process.
Intelligent Data Relationships: By establishing relationships between different entities, such as parts, suppliers, and engineering changes, OpenBOM creates a rich and interconnected data network. This interconnectedness enhances the ability to perform advanced queries and gain insights that would be difficult to achieve with isolated data silos.
Scalability and Flexibility: OpenBOM’s cloud-based infrastructure ensures that the knowledge graph can scale with the growing complexity and volume of design data. Additionally, the platform’s flexibility allows for customization to meet the specific needs of different industries and organizations.
Benefits of OpenBOM’s Knowledge Graph and Future AI Roadmap
The unified knowledge graph constructed by OpenBOM offers several key benefits:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: With all design data integrated into a single representation, decision-makers can access comprehensive and up-to-date information, facilitating more informed and timely decisions.
- Improved Collaboration: The real-time updates and centralized data management foster a collaborative environment, reducing the risk of miscommunication and ensuring that all team members are on the same page.
- Increased Efficiency: By automating data aggregation and reducing manual entry, OpenBOM minimizes errors and accelerates the design process, leading to faster time-to-market.
- Advanced Analytics: The rich interconnections within the knowledge graph enable advanced data analytics, helping organizations identify trends, optimize designs, and anticipate potential issues.
Knowledge Graph has a significant impact and source of information that can be used for semantic reasoning and logical conclusions based on the information stored in the graph. If I apply this idea to the design knowledge graph captured from all CAD data sources and stored in OpenBOM databases, mix it with information about suppliers, contractors, and vendors, I can get a very interesting set of information stored in OpenBOM graph database in machine-understandable format.
In such a way design knowledge stored in OpenBOM database can be used for semantic reasoning with Knowledge Graphs, allowing creating and maintaining a graph representing domain knowledge. It is not a very well-researched field, but introducing a product knowledge graph that simply connects information creates a foundation for this knowledge and semantic reasoning to happen. It allows users of OpenBOM to get some interesting results when query this information first using interactive tools and later using natural language. Learning with Knowledge Graphs involves representing domain knowledge in a structured way, using logical rules and reasoning to derive new knowledge, known as inferencing.
A practical example can be a system that makes recommendations for suppliers based on specific BOM knowledge, information about other design elements, and other system requirements. The system can use the data accumulated from multiple existing design sources and learn from this to become smarter. Knowledge Graph-based system structures information into a coherent web, linking entities like parts, suppliers, vendors, assemblies, and others allowing for rich semantic relationships and context-aware recommendations.
The evolving role of Language Models (LLMs) in enhancing natural language understanding within Knowledge Graphs highlights their potential to revolutionize user experiences and AI’s future possibilities in design and product development using KGs.
Conclusion
OpenBOM’s approach to building a knowledge graph is transforming the way design and manufacturing companies manage their data. By providing a unified, real-time view of design information, OpenBOM empowers organizations to innovate more effectively and maintain a competitive edge in the market. The platform’s ability to integrate data from multiple CAD systems and its emphasis on collaboration and efficiency make it an indispensable tool for modern design and manufacturing workflows.
OpenBOM’s innovative use of a knowledge graph to unify design data represents a significant step in the field of design data management. Earlier PDM/PLM systems focused on the “documents” paradigm storing records about documents in the database and managing revisions. OpenBOM’s approach is different. By breaking from traditional “document” records, OpenBOM creates a graph model allowing it to balance the need to understand and manage data in a granular form together with the ability to capture knowledge from existing manufacturing and product development organizations.
REGISTER FOR FREE to check how OpenBOM can collect data from multiple design systems and build a cohesive graph data model that will become a knowledge graph with semantic meaning and AI capabilities.
Best, Oleg
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.