In 2020, the world witnessed an unprecedented disruption as the COVID-19 pandemic swept across the globe, exposing vulnerabilities in supply chains. According to a survey by the Institute for Supply Management, nearly 75% of companies reported supply chain disruptions in some capacity due to the pandemic. This staggering statistic underscores the critical importance of supply chain resilience in an increasingly unpredictable world.
In today’s global economy, supply chain resilience is no longer a luxury but a necessity. The interconnectedness of markets means that a disruption in one part of the world can have far-reaching effects, causing delays, increased costs, and loss of business. Natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, cyberattacks, and pandemics are just a few examples of the myriad risks that supply chains face. Without resilience, businesses are left vulnerable, risking their operational efficiency, financial health, and reputation.
The purpose of this blog is to dive into the concept of supply chain resilience, exploring what it entails and why it is vital for modern businesses. By the end of this blog, you will have a clear understanding of how to fortify your supply chain, ensuring your business is prepared for whatever challenges lie ahead.
Understanding Supply Chain Resilience
Supply chain resilience refers to the capability of a supply chain to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from unexpected disruptions. This means having the foresight to identify potential risks, the plans in place to address these risks, the agility to respond effectively when disruptions occur, and the robustness to bounce back and maintain operations with minimal impact on the business.
Here are 3 characteristics of a resilient supply chain:
Flexibility: The ability to adapt processes and strategies quickly in response to changing conditions. This includes having alternative routes, suppliers, and production methods.
Redundancy: Building in buffers such as extra inventory, multiple suppliers, and additional production capacity to handle unforeseen disruptions.
Adaptability: The capacity to adjust and evolve in response to longer-term changes in the market or operating environment. This involves ongoing learning and innovation.
Visibility: Comprehensive, real-time insights into all aspects of the supply chain, from raw materials to delivery. Advanced tracking and data analytics tools play a critical role here.
Collaboration: Strong, cooperative relationships with suppliers, partners, and customers. Effective communication and shared goals help ensure all parties can work together to manage disruptions.
Assessing Your Current Supply Chain Resilience
Evaluating the resilience of your supply chain starts with a comprehensive self-assessment. This process involves identifying potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. Here’s how you can begin:
Conduct a Risk Assessment: Utilize risk assessment tools and methodologies to map out potential threats and their impacts on your supply chain. Tools like Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) software, and SWOT analysis can help in identifying and prioritizing risks.
Supplier Audits: Regularly audit your suppliers to ensure they have robust risk management and resilience plans in place. This includes evaluating their financial stability, production capabilities, and contingency plans.
Business Impact Analysis: Perform a BIA to understand the critical functions of your supply chain and the potential consequences of disruptions. This analysis helps in determining recovery priorities and resource allocation.
Scenario Planning and Stress Testing: Develop various disruption scenarios and stress test your supply chain to see how it would perform under different conditions. This helps in identifying weak points and planning appropriate responses.
Strategies to Build a Resilient Supply Chain
Building a resilient supply chain involves implementing various strategies that enhance your ability to withstand and recover from disruptions. One fundamental approach is diversification, which reduces dependency on single suppliers or regions.
By sourcing from multiple suppliers and geographic areas, companies can mitigate the risks associated with localized disruptions. This geographic diversification ensures that a natural disaster or political upheaval in one region does not cripple the entire supply chain. Additionally, supplier redundancy, which involves developing relationships with multiple suppliers for critical components, provides a buffer against supplier-specific issues. Multi-sourcing agreements also help ensure availability and price stability, further strengthening supply chain resilience.
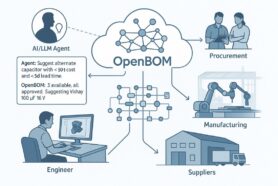
Digital transformation is another critical strategy for enhancing supply chain resilience. Technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain are revolutionizing supply chain management. IoT devices provide real-time tracking and monitoring of inventory, shipments, and equipment, offering enhanced visibility across the supply chain. AI plays a crucial role in predictive analytics, helping to forecast potential disruptions and optimize routes and inventory management. Machine learning algorithms can dynamically assess risk profiles and automate decision-making processes based on past disruptions. Blockchain technology ensures transparency and traceability, reducing the risk of fraud and errors and building trust among supply chain stakeholders.
Effective inventory management is essential for balancing just-in-time (JIT) and just-in-case (JIC) strategies. While JIT focuses on minimizing inventory levels to reduce costs, JIC maintains buffer stock to handle emergencies. A hybrid approach that combines both strategies can maintain efficiency while ensuring resilience. Demand forecasting, powered by predictive analytics, helps companies maintain optimal inventory levels by accurately predicting customer demand. Additionally, determining safety stock levels based on lead times, demand variability, and risk assessments ensures that companies can respond quickly to disruptions without holding excessive inventory.
Strong supplier relationships are fundamental to a resilient supply chain. Building partnerships and fostering collaboration with suppliers enhance communication, trust, and long-term stability. Regular and open communication ensures alignment on expectations and quick responses to issues. Trust is built through transparency and reliability, enabling collaborative problem-solving and mutual support during disruptions. Long-term agreements with key suppliers secure stability and prioritize strategic suppliers in times of crisis. Collaborative planning sessions and supplier development programs further strengthen these relationships, ensuring that suppliers are capable and resilient partners.
Developing and implementing comprehensive risk management plans is vital for supply chain resilience. Scenario planning involves developing various disruption scenarios and outlining potential impacts and responses for each. This proactive approach helps companies prepare for a range of possible events. Regular stress testing, which simulates disruptions, identifies weaknesses in the supply chain and improves response strategies. Contingency planning is another critical component, involving detailed plans for alternative sourcing options, backup transportation routes, and emergency communication protocols. These plans ensure that critical processes can continue smoothly during disruptions.
By implementing these strategies, companies can build a resilient supply chain capable of withstanding various challenges. Diversification, digital transformation, balanced inventory management, strong supplier relationships, and comprehensive risk management plans are essential components of a robust supply chain strategy. These measures not only enhance resilience but also ensure that companies can adapt and thrive in the face of disruptions, maintaining operational continuity and competitiveness in an ever-changing environment.
Future Trends in Supply Chain Resilience
As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, several emerging trends are poised to shape the future of supply chain resilience. These trends are driven by technological advances, a growing emphasis on sustainability, and potential regulatory changes.
Technological Advances: Emerging Technologies That Will Shape the Future of Supply Chain Resilience
Artificial intelligence (AI) is set to play a pivotal role in enhancing supply chain resilience. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to predict potential disruptions before they occur, enabling companies to take proactive measures. These tools can significantly improve demand forecasting, resulting in better inventory management and reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking. Additionally, optimization algorithms driven by AI can enhance routing and scheduling, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
Machine learning is another technology that will transform supply chain resilience. Machine learning algorithms can dynamically assess and update risk profiles based on new data, providing real-time insights into potential vulnerabilities. This continuous learning capability allows for automated decision-making, where models suggest optimal responses to new challenges by learning from past disruptions, thereby reducing response time and minimizing impact.
Autonomous logistics technologies, such as drones and autonomous vehicles, will enhance delivery speed and reliability, especially in hard-to-reach areas or during emergencies. Warehouse automation, through robotics and automated guided vehicles (AGVs), will streamline operations, improving accuracy and efficiency in inventory management. These technologies collectively contribute to a more resilient and agile supply chain.
Sustainability: The Growing Importance of Sustainable and Ethical Supply Chains
The intersection of resilience and sustainability is becoming increasingly significant. Sustainable practices often lead to more efficient use of resources, reducing waste and lowering costs, which in turn enhances resilience. For instance, sustainable supply chains are less vulnerable to regulatory fines, reputational damage, and market volatility associated with environmental and social issues. Furthermore, there is a growing consumer demand for ethically sourced and environmentally friendly products, driving companies to adopt sustainable practices. This not only meets consumer expectations but also builds resilience by fostering loyalty and trust.
Strategies for creating sustainable supply chains include green sourcing, where companies prioritize suppliers with strong environmental and social responsibility records. Implementing circular economy practices, such as recycling and reuse strategies, minimizes waste and creates closed-loop systems. Additionally, reducing the carbon footprint through investments in renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies can significantly enhance the overall sustainability and resilience of supply chain operations.
Regulatory Changes: Potential Regulatory Developments Impacting Supply Chain Strategies
Environmental regulations are becoming stricter, particularly concerning carbon emissions and waste management. Governments worldwide are implementing tighter controls on carbon emissions, which necessitate the adoption of greener practices and technologies by companies. Similarly, regulations on waste disposal and recycling are pushing for more sustainable supply chain practices.
Changes in trade policies, such as tariffs and trade agreements, can have a profound impact on supply chain costs and sourcing strategies. Companies need to stay informed and adaptable to navigate these changes effectively. Additionally, localization requirements in some regions are pushing for increased local production to protect local industries, affecting global supply chain strategies.
Data privacy and security are also critical concerns, with cybersecurity regulations becoming increasingly stringent. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, robust security measures in supply chain management systems are essential to comply with new regulations and protect sensitive data.
By staying ahead of these future trends, companies can enhance their supply chain resilience and remain competitive in a rapidly changing environment. Embracing technological advances, prioritizing sustainability, and adapting to regulatory changes will be crucial for building resilient supply chains capable of navigating the complexities of the modern world.
Conclusion
In an era marked by unprecedented disruptions and rapid changes, building a resilient supply chain is more critical than ever. As we’ve explored, resilience is not just about surviving disruptions but thriving despite them. By adopting strategies such as diversification, digital transformation, balanced inventory management, strong supplier relationships, and comprehensive risk management plans, companies can fortify their supply chains against a wide range of challenges. These measures ensure that businesses are not only prepared for the unexpected but can also maintain operational continuity and meet customer demands consistently.
The future of supply chain resilience will be shaped by technological advancements, a growing emphasis on sustainability, and evolving regulatory landscapes. Embracing these trends and integrating them into supply chain strategies will be crucial for maintaining competitiveness and agility. Companies that invest in cutting-edge technologies, prioritize sustainable practices, and stay ahead of regulatory changes will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of the global market. Ultimately, a resilient supply chain is a strategic asset that enhances a company’s ability to respond to crises, capitalize on opportunities, and achieve long-term success.
Are you interested in OpenBOM? Reach out. We would like to hear from you.
By: Jared Haw
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.