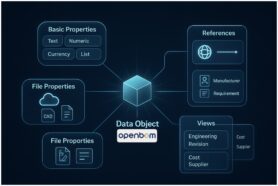
Databases are the foundation of any PLM and data management system. The time when vendors were developing their own databases was over a long time ago. However, the question of databases is usually very deep in the mind of every manufacturing company we talk to at OpenBOM. The roots of these questions are in the deep curiosity and state of mind of every engineer to understand how the system is organized and how to use it for the best advantages for themselves and the company.
What Changed in Data Management?
Data management technology has gone through a time of substantial changes and advanced development in the last decade. The main reason for that has been the development of global web infrastructure and platforms. The needs of these platforms are way beyond anything industries knew before from enterprise data management. As a result, we have developed a completely new level of data tools including databases, search, data acquisition, and migration tools.
Even more important is the database architecture approach related to the use of multiple databases called polyglot persistence. The core idea is quite simple. To understand it, you need to think back in time when every software vendor had a dilemma about what programming language to use. Advanced components and web tech made this question irrelevant. We use multiple languages for web, servers, and other applications, which is polyglot programming now. The same is happening now with data – service-based architecture makes it very easy and efficient to use multiple databases to get advantages of technologies to optimize and simplify data management layers.
Modern PLM Data Management
In our recent event Demystifying Modern PLM, we touched on the topic of how OpenBOM is using a combination of databases such as Mongo, Neo4j, Elastic, and some others to provide a flexible data management environment.
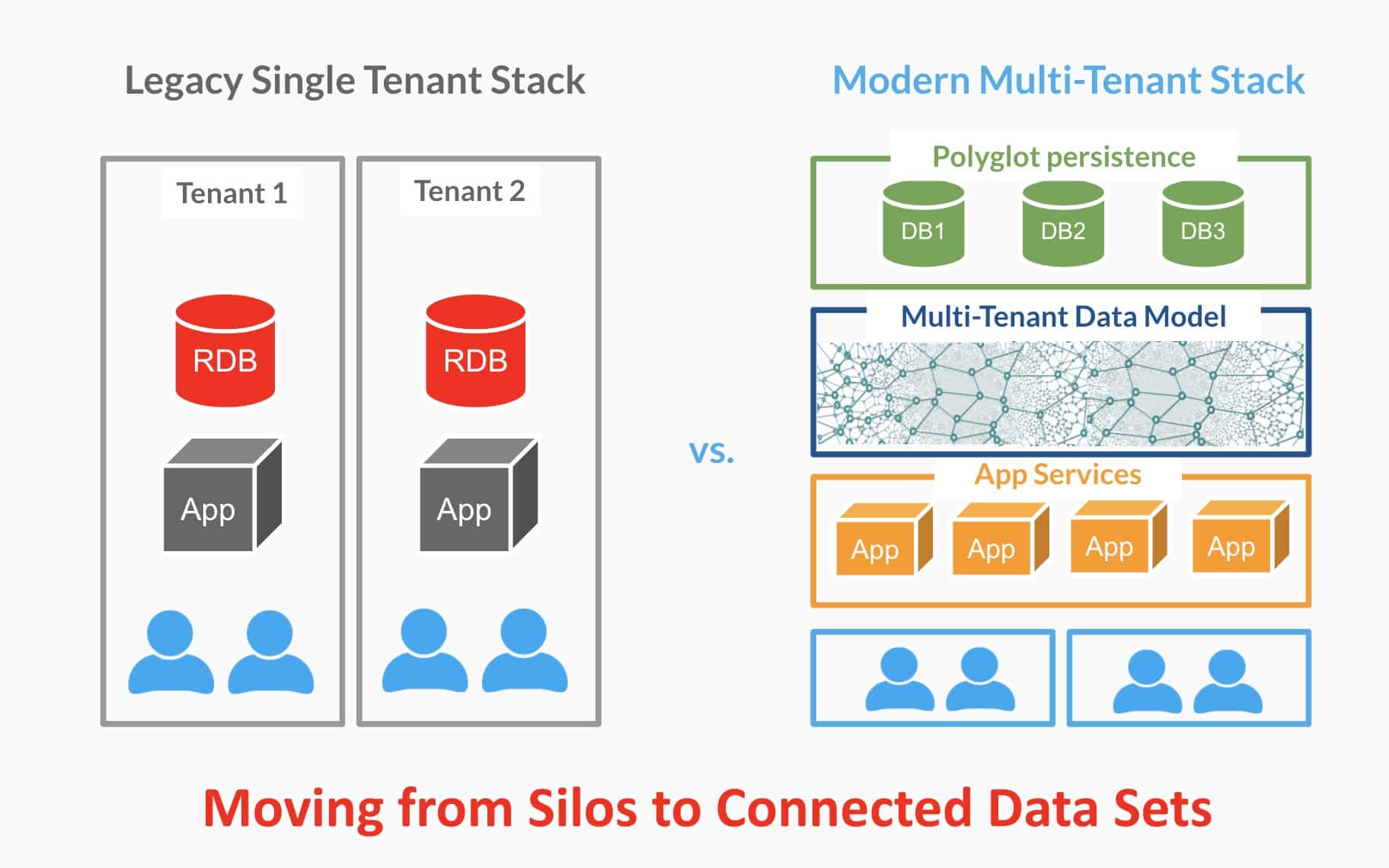
Check out the video and slide deck here explaining multi-tenancy and data use.
In this video fragment, I shared, OpenBOM Chief Architect, Chirs Chaulk explains the details behind polyglot persistence and how OpenBOM’s data stack uses multiple databases, scales and can be used in a variety of environments.
Modern databases bring a new set of advanced features that can be used for analytics, management of flexible relationships, collaboration, and providing unique data management services. Check out our technological session for more information.
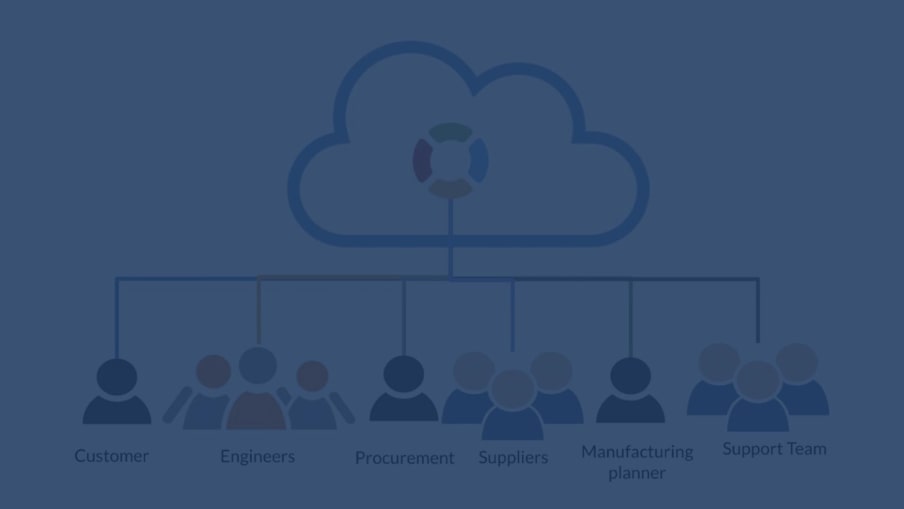
A separate and important topic is related to the multi-tenant character of the OpenBOM platform. Such architecture allows you to deploy OpenBOM in a variety of environments and use it by multiple customers as well as large OEMs. A modern REST API and the use of data as a service approach can give advanced capabilities of data analytics and integrations using the OpenBOM data platform.
Conclusion
OpenBOM is a modern PLM system with an advanced and flexible database foundation using the best databases to provide a scalable and flexible environment combined with sophisticated data management functions. SaaS architecture gives multiple advantages – to have a system as a service for many customers and also to have an option to deploy the same platform as a foundation of a complex enterprise data management solution for a very large enterprise manufacturing OEM. While
Enterprise IT these days has increased interest in open and scalable system architecture, OpenBOM can offer very unique capabilities.
REGISTER FOR FREE to learn how OpenBOM can help. Contact support if you have more questions.
Best, Oleg
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.