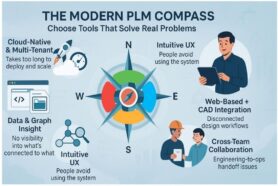
Manufacturing companies are increasingly feeling the pressure of digital transformation, yet many struggle with low confidence in traditional PLM tools. According to CIMdata market analysis, only 17% of manufacturing companies cannot live without PLM tools. Despite the growing need for efficient data management, Excel remains widely used, favored for its simplicity but ill-suited for handling the complexities of modern manufacturing. This reliance on spreadsheets often leads to disconnected data, poor collaboration, and missed opportunities for innovation. With the gap between the need for digital tools and the current state of PLM adoption widening, what digital transformation strategies can help manufacturers transition effectively from outdated methods like Excel to more advanced, scalable digital solutions? Let’s talk about it.
The Demand for Digital Transformation
According to CIMdata’s 2023 research presented at the annual Market and Industry Forum in Ann Arbor in March 2024, manufacturing companies still prioritize achieving faster, cheaper, and better outcomes.
However, achieving these objectives remains a significant challenge. The path to these goals involves leveraging digital transformation, but the journey is not without obstacles. Consider the numbers: the manufacturing industry continues to struggle with inefficient data practices. Despite the push for modernization, spreadsheets remain dominant according to Manufacturing 2030 NAM report, with 70% of manufacturers still manually entering data into Excel and similar files. Moreover, only 25% of manufacturers have high confidence that their data is properly organized, traceable, and reliable. These issues highlight the urgent need for change.
This need for digital transformation is reflected in broader industry trends. An EY research about trends in discrete manufacturing reveals that 68% of CEOs from the world’s largest industrial product companies are increasing their investments in digital technologies. The data clearly underscores the demand for business transformation, leading to a pressing question: how can manufacturers make this transformation happen?
Low Confidence in Existing PLM Products and Technologies
Despite the clear demand for digital transformation, many manufacturers lack confidence in current PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) products and technologies. CIMdata’s 2023 research reveals a striking disconnect between the potential value of PLM systems and how they are perceived. Only 17% of respondents said they couldn’t live without PLM, while 34% believe PLM is primarily an engineering tool. Worse still, 37% view PLM as too expensive and lacking a clear return on investment (ROI).
A significant issue contributing to this disconnect is the overlap between digital transformation initiatives PLM, ERP, and MES systems, creating confusion about their distinct roles. As a result, digital initiatives often conflict, making it hard for companies to determine where they should focus their efforts. With these challenges in mind, it’s clear that manufacturers need more confidence in their technology stack if they want to move forward with digital transformation successfully.
The Role of Digital Technologies in Transforming Manufacturing
The EY report on digital transformation in discrete manufacturing sheds light on two major trends reshaping the industry: increased customer data access and the rise of cloud manufacturing solutions. These trends redefine how manufacturers operate, interact with suppliers, and meet customer needs.
Customer Data Access
As digital solutions advance, customers in discrete manufacturing are gaining access to more data from within their value chains. This increased access is causing disruptions across the industry, especially for traditional hardware suppliers who have long held the advantage of application knowledge. With more data available, knowledge traditionally held by suppliers is becoming commoditized and standardized, opening the door for tech companies to bring greater value to the manufacturing ecosystem.
The impact is clear—customers now expect seamless data flows across applications, which is pushing industry players to collaborate more effectively to address customer problems. Companies that fail to provide such integration risk losing out to those that can offer smoother data exchanges.
Cloud Manufacturing
Since the early 2010s, cloud manufacturing platforms have introduced new ways for companies to order parts and assemblies. These platforms allow customers to receive instant quotes for components, streamlining the process of prototyping and providing alternative sourcing options. While the long-term effects of these platforms are still under review, they are already disrupting traditional customer-supplier relationships.
Cloud platforms significantly reduce the lead time between CAD designs and quoting, accumulating know-how across different manufacturing processes, tools, and machinery. This disruption is particularly felt by small and mid-sized machine shops, as well as component manufacturers, who now face competition from more efficient cloud solutions. The question remains whether these platforms can move beyond prototyping to become viable options for full-scale production.
A Strategy for the Discrete Manufacturers Digital Transformation
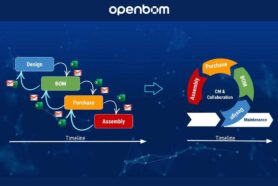
At OpenBOM, we are focused on providing practical solutions to help engineering teams and manufacturing companies embrace digital transformation. Our approach includes three key strategies:
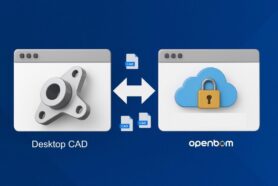
- Digital BOM: Moving away from spreadsheets, OpenBOM helps manufacturers create digital data representations ( aka Digital BOM) that are accessible, traceable, and reliable. This digital foundation is crucial for enabling a seamless transformation process.
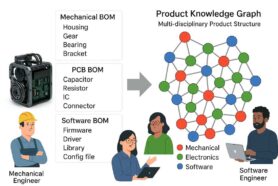
- Seamless Design Integration : OpenBOM leverages a flexible data model foundation using Product Knowledge Graph technology, which allows manufacturers to easily integrate their data across various systems, most importantly CAD and other design systems. Immersive CAD add-ins and other integration approaches combined with open APIs including “One-Click BOM” and Quick Start functions, helping to reduce friction in the design-to-manufacturing process.
- Connected RFQ and Supply Chain Process: OpenBOM integrates supply chain and purchasing processes with real-time data, including embedded ordering and inventory control. The solution connects directly with financial and ERP systems, allowing for smoother communication and reducing lead times from CAD to quote.
This comprehensive strategy addresses key pain points in the digital transformation journey, helping manufacturers to organize business processes and connect engineering activities with the purchasing department to order components and assemblies more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Conclusion
Digital transformation in manufacturing is not an option—it’s a critical instrument to achieve their business goals and the way for companies aiming to stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world. OpenBOM helps streamline the transition by optimizing the CAD-to-quote lead time and ensuring that data becomes an enabler of process optimization, not a hindrance.
OpenBOM 3 steps strategy for digital transformation helps manufacturing companies to find their way in organizing data, connecting the design (CAD) system to a digital model in a seamless way, collecting and enriching product information, and organizing an RFQ/Purchasing process in a way to optimize the communication. The big difference is usage of digital BOM model instead of spreadsheet allowing to all parties to collaborate online. The real time ‘digital BOM chat’ allows to everyone to stay connected.
Ready to see how OpenBOM can transform your business? Contact us to discuss what you can do.
Register for free and discover how we can help you streamline your operations and bring your manufacturing into the digital age.
Best, Oleg
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.