In the manufacturing industry, changes and updates to products (and their corresponding design data) happen frequently. To ensure that these changes are efficiently and correctly implemented, a product release process is often put into place.
One key function of PLM software is its ability to manage product releases. A product release is essentially a formal process to collect all data about product including all data records and corresponding documents. In order to make sure that each product release goes as smoothly as possible, most manufacturers have put in place a specific process for doing so. This article will take a closer look at what goes into this process and why it’s important for keeping things running smoothly in the mad dash of modern-day manufacturing. So buckle up – we’re about to take off on an exciting journey through the world of product releases!
Modern Product Development Process and Release
While you can think about product release as one of the most common processes in engineering and manufacturing companies, it usually raises a lot of questions and controversy because it usually touches all aspects of product development, validation, and information exchanges. Modern product development is multi-disciplinary and products are developed by multiple teams and organizations. How to bring all these activities together and, at the same time, allow all members of the teams to work in a coordinated manner? Many of these questions are usually coming when companies are starting to implement product data management and product lifecycle management software.
Moving from Documents To Granular Product Data
Historically, engineering and manufacturing organizations were working with documents. While documents are still very important and provide a critical part of the engineering and product release process, they are replacing their major role of data management vehicle with more granular and robust data management technologies and approaches. Companies looking into the digital future are realizing that documents are just containers for information and in many situations can be eliminated and replaced by more efficient data management systems. Organizing product information in granular forms allows organizations to optimize their process and also focus on how the right data can help them in making the right decisions.
OpenBOM Data Model and Objects
At OpenBOM, we developed a robust and flexible platform to manage information, to share it in the organization, with suppliers, contractors, and customers. In the picture below you can see a high-level schema of OpenBOM data objects.
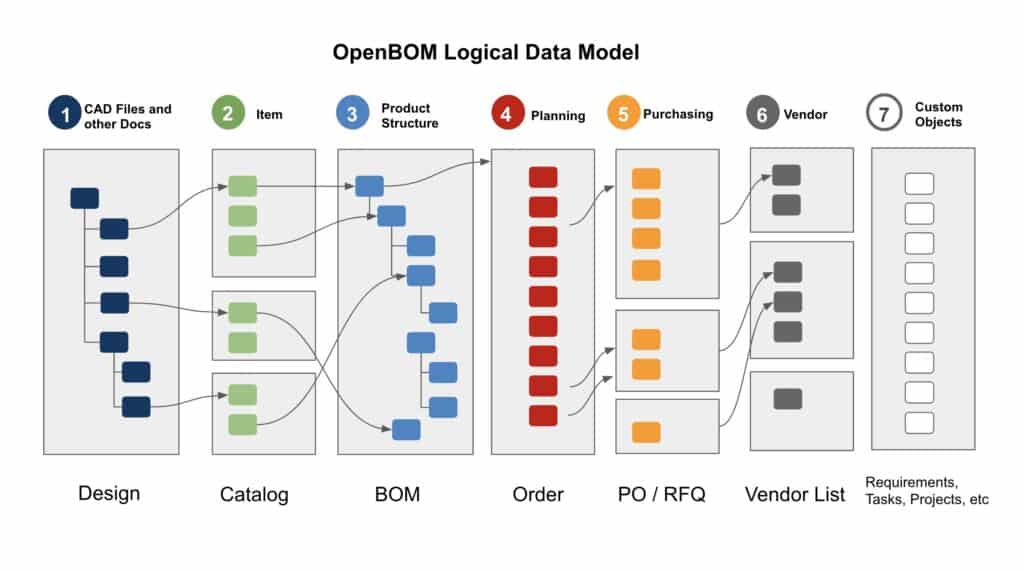
The data objects in OpenBOM allow you to define all elements of product information in a granular form – design files and documents, items and product structure, procurement and production planning, and others.
Before jumping to discuss product release process best practices, I want to stop and talk about the different types of lifecycles OpenBOM helps you to organize. Each of these lifecycle processes focuses on different activities, but at the same time, they are connected to support product development processes.
Design Lifecycle
Engineering organizations’ core activity is to design products. This is what a typical R&D organization does and it requires a big deal of organization and coordination. Modern product development teams are multi-disciplinary and include different engineers – mechanical, electronics, software, and others. Managing their data and processes is a complex task. What OpenBOM offers here is document version control allowing R&D organization to manage their CAD and other engineering documents and to manage the process of sharing and versions.
OpenBOM Drive is responsible for this process and it allows you to organize CAD files in a vault with restricted access, share information on this vault with multiple people and teams, and manage check-out/in-process to control versions and release of these documents.
Engineering (or Product) Lifecycle
The maturing of design leads to the creation of one of the most fundamental elements of the product lifecycle – product structure combined of items. An Item is the key lament of the product structure and it can be anything (material, OTS part, assembly, kit, etc.) OpenBOM allows you to organize items, manage meta-data (attributes), and attached documents (files- eg. CAD files, specifications, etc), and create BOMs as elements of the entire product structure.
BOM and Items are key elements of the product lifecycle because they define all product information, with all data attributes, attachments, and related pieces of information. OpenBOM is managing the Item lifecycle (revisions) and if an Item has a BOM (assembly) also includes BOMs in the revision.
OpenBOM revision process supports capturing product maturity, allowing teams to work on items and product structures collaboratively and as soon as a product moves up in maturity, to create a revision (baseline of the product stored with a specific revision label). The process can be controlled by change requests and approvals in order to prevent an uncontrolled revision creation process.
Production (Order) Lifecycle
Nothing can be done without planning manufacturing, ordering components, and planning work orders. OpenBOM provides some support for this process by helping manufacturing companies to manage vendors, orders, POs, and RFQs, I will talk separately about this process. In the future, the OpenBOM production order lifecycle will be expanded to a full MBOM management process.
Release Process – A Big Picture
In the picture below you can see the main steps of the release process including design work, item, BOM release, building orders, and managing service/maintenance operations.
Design and BOM Lifecycle Coordination
OpenBOM allows both design and product lifecycle to go independently and coordinated. Engineering organizations can operate with design versions using CAD software and OpenBOM Drive service. This process allows changes in CAD file versions and collaboration between engineers. Items and BOM lifecycle, at the same time, allow for coordination of all design dependencies by creating multi-disciplinary BOM and managing revisions of items and BOMs. Check the picture below.
Conclusion
I described the basics of the OpenBOM release process that contains and combines activities by multiple engineers and other people together. A coordinated collaborative release process is a unique function of OpenBOM because it allows multiple people and organizations to work together. A coordinated stage process of multiple lifecycle processes – engineering (design), product (BOM), and production (Order) allows companies to work together and coordinate their functions throughout the set of maturity events (eg. Document Version and Item/BOM Revision). The unique value of OpenBOM is to keep activities collaborative, independent, and coordinated at the same time.
In my next article, I will bring you more details about how to manage the entire release process. In the meantime, REGISTER FOR FREE and start a trial to check how OpenBOM can help you today.
Best, Oleg
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.