In the dynamic landscape of modern business, innovation stands as a fundamental driver of growth and competitive advantage. For companies looking to introduce new products to the market, the New Product Development (NPD) phase holds immense significance. Within this critical phase, the ability to swiftly transform ideas into tangible prototypes can make all the difference between success and obscurity. Enter rapid prototyping – an agile approach that has reshaped the way businesses innovate.
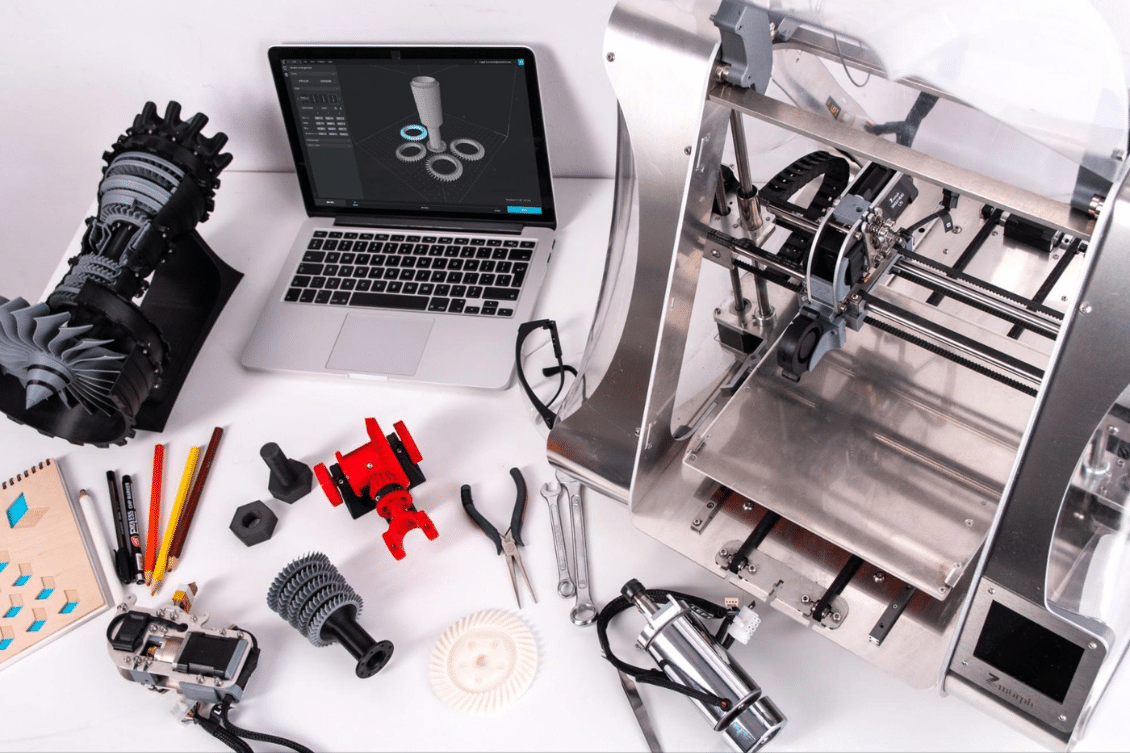
Rapid prototyping is a dynamic process that allows companies to create physical models of their designs with exceptional speed and precision. By harnessing technologies and leveraging a range of prototyping techniques, businesses can rapidly iterate, test, and refine their concepts, accelerating the product development journey to new levels.
In this blog, we will delve into an understanding of rapid prototyping, its benefits, and also the different types of prototypes.
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a relatively new process used in product development to quickly and efficiently create physical prototypes of a product design. It enables designers, engineers, and stakeholders to visualize, test, and validate ideas, concepts, and designs before moving forward with full-scale production. The primary goal of rapid prototyping is to accelerate the product development cycle, reduce time-to-market, and minimize the risks associated with new product development.
Instead of relying on traditional manufacturing methods, which can be time-consuming and expensive, rapid prototyping employs various cutting-edge technologies and materials to produce functional prototypes within a short period. These prototypes closely mimic the final product, allowing designers to assess its form, fit, and function, and gather valuable feedback for further improvements.
Benefits of Rapid Prototyping
Companies are trying to look for tools and processes that support them in agile NPD. Rapid prototyping is one of these tools. Manufacturers no longer have to wait weeks to see a prototype. By taking advantage of rapid prototyping techniques, manufacturers can have a physical prototype very quickly.
Here are the top benefits of rapid prototyping:
Faster Iterations and Design Refinements
Rapid prototyping allows designers and engineers to create physical prototypes quickly. This enables them to iterate and refine designs at a much faster pace, leading to more efficient product development cycles and quicker time-to-market.
Reduced Development Costs and Time-to-Market
By accelerating the design process and minimizing the need for costly tooling, rapid prototyping helps in reducing development costs. The ability to create prototypes rapidly also shortens the time it takes to bring a product to market, giving companies a competitive edge.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Physical prototypes facilitate better communication between cross-functional teams and stakeholders. Visualizing and interacting with a tangible model makes it easier to discuss design concepts, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions collaboratively.
Enhanced Design Validation and Testing
Rapid prototyping allows for the creation of functional prototypes that closely mimic the final product. These prototypes enable rigorous testing and validation, ensuring that the design meets performance and quality requirements before investing in mass production.
Risk Reduction and Improved Decision Making
The ability to physically assess and test prototypes helps identify and mitigate potential risks early in the product development process. Data-driven decision-making based on prototypes leads to better-informed choices, reducing the likelihood of costly design flaws or manufacturing errors.
Better Customer Engagement and Feedback
Involving customers early in the prototyping process allows companies to gather valuable feedback and insights. This customer-centric approach leads to products that better meet customer needs and expectations.
Types of Prototypes During Agile New Product Development
During the product development process, various types of prototypes are used at different stages to support customer-focused development. Each prototype serves a different purpose and leads you into the next steps of development.
Here are the different types of prototypes during the new product development process:
Proof-of-Concept (POC) Prototypes
These prototypes are used in the early stages of product development to demonstrate the feasibility of a novel idea or technology. They focus on validating the core concept and its potential before investing further resources.
Visual Prototypes
Visual prototypes are used to showcase the product’s appearance and user interface (UI) design. They provide a realistic representation of the product’s aesthetics and help stakeholders visualize the final product.
Form and Fit Prototypes
Form and fit prototypes are created to ensure that the product’s physical dimensions and components fit together properly. They focus on testing the physical compatibility and ergonomics of the design.
Functional Prototypes
These prototypes aim to validate the product’s functionality and performance. They are more advanced than POC prototypes and demonstrate the product’s basic features and operations.
Pre-Production Prototypes
Pre-production prototypes are the closest representation to the final product and are used to test the manufacturing processes and ensure that the product can be mass-produced efficiently. These samples are usually made during the pilot run.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping is a technique used by manufacturing companies to support them with agile new product development. This is just one of the tools that manufacturers leverage in order to get their products to market faster.
OpenBOM stands to empower manufacturers to adopt agile new product development processes. By enabling collaboration between different teams, managing changes, automatically creating derivative files (STEP, PDF, DXF, etc), and more, manufacturers bridge the gap between design and production.
If you need to improve the way you manage your data and processes, contact us today for a free consultation.
Regards,
Jared Haw
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.