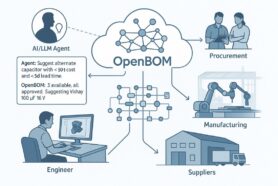
2024 has been a remarkable year for the manufacturing industry, marked by rapid technological advancements, evolving global dynamics, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Manufacturers faced both challenges and opportunities as they navigated supply chain disruptions, workforce changes, and increasing customer demands for smarter, faster, and greener solutions.
Amidst this shifting landscape, key trends emerged that have redefined how businesses operate and compete. From embracing digital transformation to prioritizing sustainability and innovation, the lessons learned in 2024 will shape the future of manufacturing.
In this blog, we’ll explore the most significant trends that defined 2024, the challenges, and the insights gained from this transformative year. Whether you’re reflecting on your journey or looking for inspiration for 2025, these lessons offer valuable takeaways for every manufacturing leader.
Resilient Supply Chains
In 2024, resilient supply chains once again showed their importance with the continued ongoing global challenges. From geopolitical tensions and the threat of additional tariffs to fluctuating demand, the need for agility and reliability in supply chain operations reached new heights.
To address these challenges, manufacturers invested heavily in strategies to build resilience. Diversifying supplier networks became a top priority, with many businesses adopting nearshoring and reshoring practices to reduce reliance on distant or single-source suppliers. By bringing production closer to home or spreading risk across multiple partners, companies were better equipped to handle unexpected disruptions.
During this time, collaboration between manufacturer and supplier becomes important as well. Manufacturers worked closely with suppliers and logistics partners to strengthen relationships and streamline processes. This collaborative approach ensured that everyone along the chain was aligned, reducing delays and improving overall efficiency.
The lessons from 2024 are clear, suppliers and contract manufacturers are strategic assets. Manufacturers that prioritize resilience and adaptability in their supply chains are better positioned to navigate uncertainty, maintain competitiveness, and seize new opportunities in an ever-changing global environment.
Also, in 2025, these challenges will not go away. They might even be heightened with the likelihood of additional tariffs coming under the new administration. So, if you haven’t thought about diversifying your supply chain then this is something that you must do in 2025.
Accelerating AI
AI continued its rise in 2024, transforming manufacturing operations at every level. From streamlining production to enhancing supply chain efficiency, AI has become an indispensable tool for manufacturers aiming to stay competitive in a fast-evolving landscape.
One of the most notable trends is the widespread adoption of AI technologies across the industry. Already, about 77% of companies are either using or exploring the use of AI in their businesses, according to a report by the National University. This rapid uptake highlights AI’s potential to drive innovation and deliver measurable results.
AI-powered solutions are reshaping how manufacturers approach production. Predictive maintenance systems, for example, use machine learning algorithms to identify equipment issues before they occur, reducing downtime and optimizing performance. In addition, AI-driven robotics are enhancing precision and efficiency on factory floors, allowing manufacturers to produce high-quality goods at scale.
AI is also playing a pivotal role in product development. Generative design, driven by AI, allows engineers to create innovative prototypes by exploring thousands of design iterations in a fraction of the time. This accelerates the time to market and ensures products meet both functional and cost requirements.
Despite the impressive advancements, the integration of AI is not without its challenges. Companies must navigate ethical concerns, data privacy regulations, and the need to upskill their workforce to fully leverage AI’s potential. However, those that successfully embrace AI are poised to gain a significant edge in efficiency, innovation, and responsiveness.
Building a Skilled Workforce
In 2024, workforce upskilling emerged as a critical priority for manufacturers striving to keep pace with rapid technological advancements. As automation, AI, and other advanced technologies redefined traditional manufacturing roles, businesses recognized the need to equip their employees with the skills required for this new era.
This shift was driven by several factors. First, the growing adoption of digital tools and processes created a demand for workers who could operate and manage these systems effectively. For instance, roles involving data analysis, AI supervision, and digital supply chain management became essential, necessitating new training programs and resources.
Second, companies faced a competitive talent market where skilled workers were increasingly in demand. To retain their workforce and attract top talent, many manufacturers invested in reskilling and upskilling initiatives. These efforts not only improved employee satisfaction but also bolstered organizational agility by ensuring teams could adapt to evolving technologies and processes.
Training programs often focus on both technical and soft skills. Employees were trained to work with new technologies like IoT and machine learning, while also enhancing their problem-solving, communication, and leadership abilities. Additionally, partnerships with educational institutions and online learning platforms played a significant role in delivering accessible, high-quality training options.
Ultimately, the shift toward workforce upskilling reflects a broader understanding that technology alone cannot drive success, empowered and skilled workers are equally essential. As manufacturers continue to embrace this trend, they are building a more resilient and capable workforce, ensuring their ability to thrive in an increasingly complex and technology-driven landscape.
The Continue Rise of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
In 2024, digital transformation has become a cornerstone of the manufacturing industry’s evolution. An estimated 90% of organizations are now undergoing some form of digital transformation, according to McKinsey & Company.
Manufacturers are leading the charge by integrating advanced technologies such as the IoT, AI, and cloud computing into their production and operational workflows. These innovations enable real-time decision-making, improved efficiency, and enhanced product quality.
The urgency for digital transformation was originally accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, with nearly all organizations reporting an increased focus on adopting digital tools to remain agile and resilient. As manufacturers look toward the future, their ability to harness these technologies will define their ability to innovate, adapt, and thrive in an ever-evolving landscape.
Despite significant investments, success is not guaranteed. Back in 2021, only about 35% of organizations reported achieving their digital transformation goals (BCG, 2021), highlighting the complexities of adopting new technologies and processes.
However, manufacturers are embracing this challenge, and tools are becoming more modernized. Therefore, this number is expected to increase.
Sustainability Became a Business Priority
In 2024, sustainability evolved from being an admirable goal to an important pillar of success in the manufacturing industry. As businesses face growing pressure from consumers, governments, and investors to adopt greener practices, sustainability has become a critical competitive advantage. Consumers also don’t just care about your products, they care about your mission.
One of the driving forces behind this shift is the global push toward reducing carbon emissions and minimizing waste. Many manufacturers have adopted circular economy principles, focusing on reusing materials, designing products with sustainability in mind, and minimizing their environmental footprint. For instance, sustainable packaging, energy-efficient production processes, and renewable energy sources are now common practices among industry leaders.
Regulatory changes have also played a significant role. Governments worldwide have introduced stricter environmental standards, prompting companies to accelerate their sustainability efforts. Additionally, organizations are increasingly setting ambitious goals, such as achieving net-zero carbon emissions or committing to 100% renewable energy by specific target dates.
The trend toward sustainability also highlights the importance of collaboration. Manufacturers are working closely with suppliers and partners to ensure sustainable practices across the entire value chain. From sourcing eco-friendly materials to improving transportation efficiencies, these joint efforts are paving the way for a greener future.
As sustainability continues to shape the manufacturing landscape, companies that embrace it as a business priority will not only reduce their environmental impact but also position themselves as leaders in a rapidly changing industry.
Conclusion
As we welcome 2025, it’s clear that the manufacturing industry has undergone profound changes, driven by technology, sustainability, and the need for resilience. From the rise of digital transformation to prioritizing sustainable practices, manufacturers have shown remarkable adaptability in meeting the demands of a rapidly evolving world.
Looking ahead, these lessons will continue to shape the path forward. By leveraging new technologies, prioritizing sustainability, and investing in their people, manufacturers can remain competitive in an increasingly dynamic global market. The strides made in 2024 have set a strong foundation for continued growth and innovation in the years to come.
By: Jared Haw
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.