Content Updated 2/26/2024
The first step to understanding bills of materials (BOM) and how BOM operates is defining the term and what it means. A Bill of Materials represents the full set of information about the product, what it includes and contains, grouping all assemblies, parts, and materials with the corresponding quantities and connected documents.
The bill of materials, also known as a product structure, contains important components (parts, materials, assemblies) required to engineering and manufacturing a product. This structure is usually made up of assemblies and sub-assemblies (sub and intermediate) and components (parts and materials). It also has details about all the necessary parts and their quantity.
The bill of material is designed to provide an information link between engineering and manufacturing partners. It is also used by company departments to communicate and manage information for product development processes. So, what is the bill of materials? Let’s see the main takeaways.
Main Takeaways:
- What makes BOM Digitally Defined: The bill of materials (BOM) is more than just a list; it’s a digitally defined data structure meticulously crafted by manufacturing companies. It encompasses comprehensive information on the items (components, materials, etc.) essential for producing an end product. In its digital form, the BOM goes beyond a simple list of parts. It incorporates a full set of information including links to documents, technical specifications, quality procedures and supplier information for each part and component.
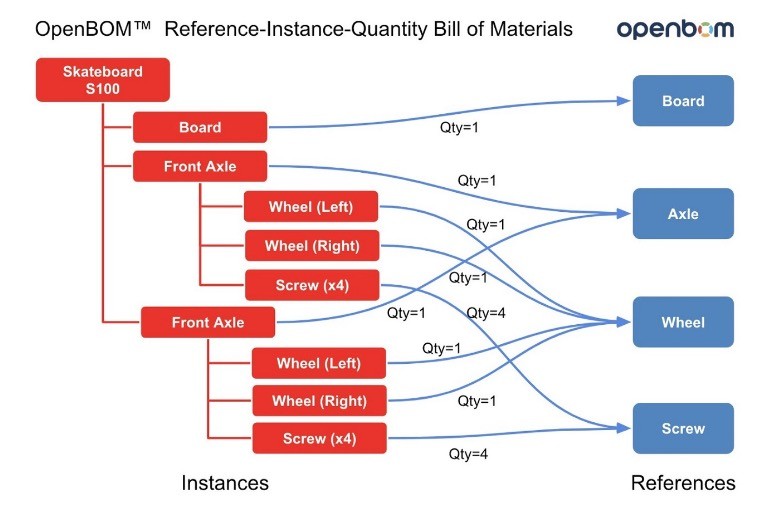
- Part Numbers are used to show all components and uniquely identify them. Bill of Materials (Product Structure) can be presented in different ways — single-level, multi-level, or flattened to visualize information about product structure in the way needed for engineers, manufacturing planners, contractors, and other users.
- When we define Items, we can distinguish between different component types (e.g. Buy, Make, Material, Labor, etc.) that are most commonly used in manufacturing. Additional information can be used to filter BOM using effectivities, configuration, vendor information, etc.
Why Are BOMs Important
Manufacturing is a complex process that requires a well-defined process, including a recipe for what needs to be manufactured. The Bill of Materials is the lifeblood of every product development process and contains all information needed to manufacture a product. To yield profit after the initial investment, you need to make sure that the final product is of the best possible quality, considering cost and quality.
Bills of materials definitions show us that a product is designed according to the requirements and with the desired results. A well-defined Bill of Materials will ensure the product will be delivered on time and according to the standards.
Key Benefits of BOM Management Solutions:
- It keeps your business organized. With a properly outlined assembly, everyone on the team knows what to expect and when to expect it.
- Manufacturing companies are under continuous pressure to perform faster to meet engineering, manufacturing, and supply chain deadlines. The bill of materials contains accurate details that enable smooth activity.
- Ensure all components are counted and provide a tool to plan product costs.
- Project management has a better vantage point and more information when it comes to decision-making. This includes figuring out ways to speed up the product development process or making it more cost-effective for the business.
- Intelligent BOM operation can help manufacturers dramatically reduce risks, and create or increase productivity and innovations.
- Individually assigned tasks are easily executed using accurate Bill of Materials, and any mistakes encountered at each stage of the process can be quickly identified and corrected ahead of time.
- Another meaning of a bill of material is that it is easier for the manufacturer to optimize the supply chain and manufacturing processes.
At OpenBOM , we redefine BOM management with:
Multi-Tenant Data Management: Break free from single database limitations. Collaborate seamlessly across companies.
Digital Bill of Information Core: Gain a single source of truth with precise data modeling and tracking.
Real-time Collaboration: Simultaneous editing and instant updates streamline teamwork.
Comprehensive Features: We focus on information flow optimization and provide connected services that usually exist in PDM, PLM, and ERP separately.
Openness and Integration: Easy, export, import, share information including access to REST API.
CAD and ERP Integrations: Seamlessly integrate with your preferred software.
Experience the future of BOM management with OpenBOM today.
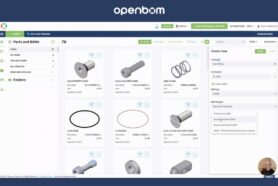
What to Include in an Effective Bill of Materials:
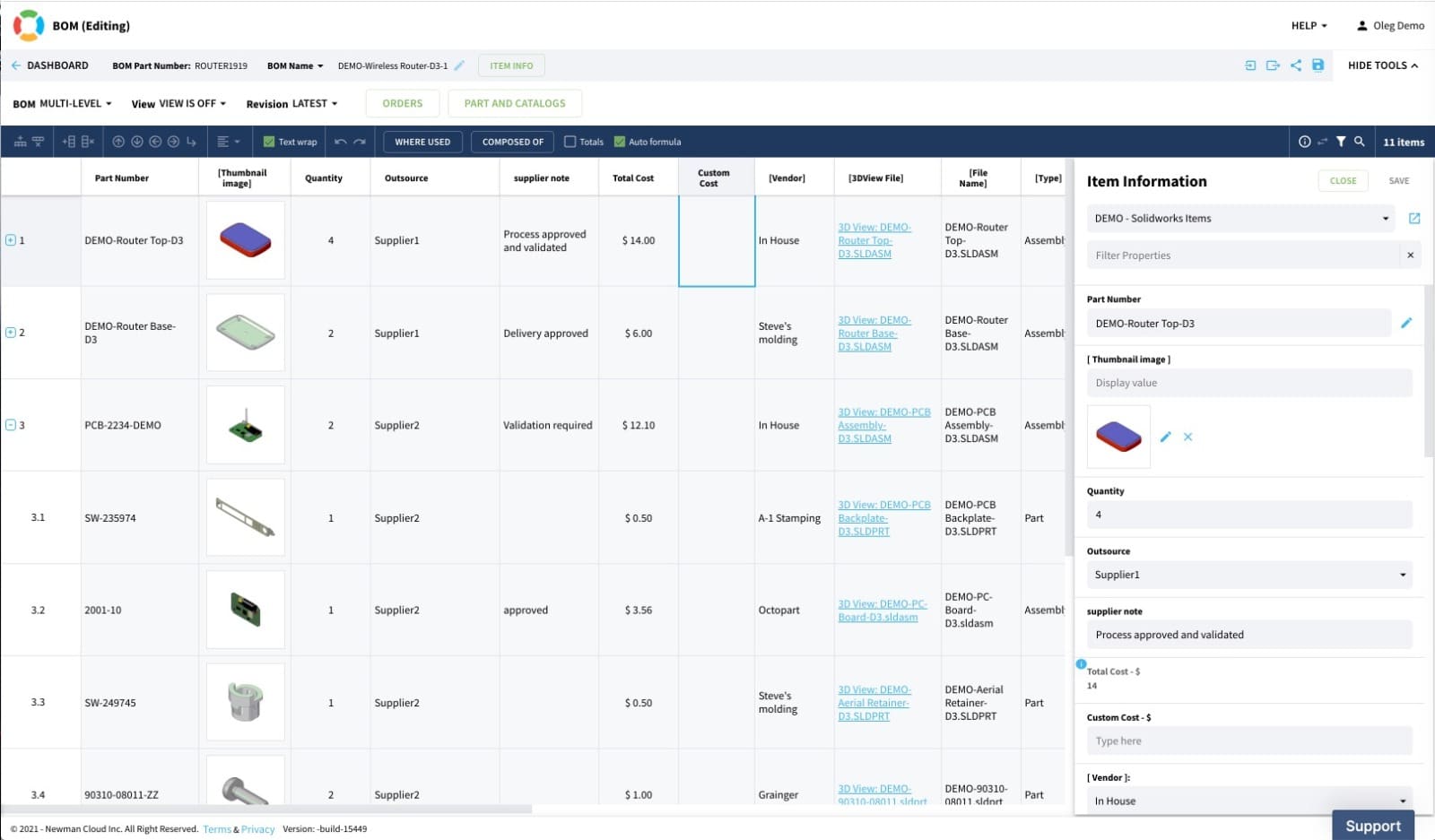
OpenBOM has a flexible data model and allows customers to define their own data attributes for Bill of Materials and Items. Now let’s analyze a typical BOM by highlighting what it is made up of:
- Part number — use a numbering scheme to identify all the individual parts further. It is important to make sure that there is no repetitive number, especially if many parts are involved.
- Name of part — provide a special name to each part to help prevent confusion down the line.
- Phase — take note of every stage and what parts belong to it, also indicate how far in the process of production they are. For instance, you can indicate the stage of production by using the phrase “in production”. The importance of this part is that it allows you to stay track of what is being done.
- Description — every single part should be described in detail. This also serves to distinguish it from other parts and makes it easy to identify.
- Quantity — take note of the number of all the parts involved at every phase of production.
- Measuring unit — find a system of measurement that will help you define each part. To make sure that you get the right quantities, remember to be uniform across the board.
- Procurement type — take note of how every part is bought or created.
- Reference designators — document this information to help you prevent any problems down the line.
- BOM Notes — other additional information.
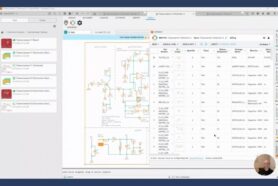
Product Structure (BOM)
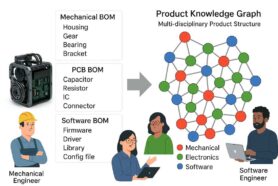
Product Structure (BOM) is defining the multiple hierarchy of components, and all related information for a product. The different components of a BOM of materials can be arranged in multiple hierarchies to represent different product structures for engineering, manufacturing, supply chain, and maintenance. Altogether, they represent a product knowledge graph managed by OpenBOM.
There are three main ways to visualize Bill of Materials:
- Single-level BOM
- Multi-level BOM
- Flattened BOM
Note: Flattened BOM is sometimes called Part List, although it can contain not only parts.
Single-level BOM
The single-level bill of materials has a simple structure. It names all the important components required for manufacture and arranges them in one level.
It works like a recipe, where all important ingredients are listed. Due to its simplicity, the single-level BOM is not suitable for large-scale production, especially complicated end products.
Multi-level BOM
To represent a complex product, companies are using multi-level BOMs. The structure can represent how the product is built and designed, allowing group-specific items in the subsystems and modules (for example, a group dedicated to created or purchased parts, a subgroup of assemblies).
It usually has the following structure:
- Details about the marketing of the end product involve finding better ways to appeal to the consumers of the product and keep them engaged.
- The various processes involved in the manufacturing of the product and any tactics that may be applied to reduce costs.
- Testing the product to ensure the best quality is released to the public for use.
Flattened BOM
Another way to present all components needed to manufacture the product is to present a flattened list of all items used in multiple assemblies. Such a BOM is critically important for planning and procurement because it gives an easy way to access all information and works as a summary of all component quantities used in multiple assemblies.
6 Steps to Prepare a Bill of Materials
Every upstream project needs to include manufacturing bills of materials as another (major) type of case management. Usually, the distributors try to use standard BOM to record all costs properly. To encourage you, let’s check the main steps to prepare BOM:
1. Identify All Sources of BOM Information:
The first step in preparing the Bill of Materials is to identify all sources of information needed to create a BOM. The information includes:
- Requirements data
- Design Information
- Manufacturing data
- Supplier’s data
It is critical to include ALL information needed to manufacture the product in the bill of materials. Don’t leave information outside of the BOM because it will lead to mistakes, delays, and unexpected costs.
2. Create the Initial BOM
After identifying all sources of information for the BOM, you need to take steps to bring the information from other systems (e.g., CAD systems) or to create data manually. The process of BOM creation is iterative. It is possible that you won’t be able to create all the information at the first step, so you will have to come back to add information.
3. Manage Revisions & Update BOM
Change is the most permanent thing. Therefore, as you work on the Bill of Materials creation, you need to be prepared to capture changes and maintain revisions of the Bill of Materials. It will allow you to track work and support the traceability of changes.
4. To Validate Quantity & Data Correctness
Keep in mind that the initial Bill of Materials created from a design system might not include all the needed information or the correct quantity for parts and components. At this stage, you need to validate the quantities and any additional items (e.g., documentation, labor, etc.) that need to be included in the BOM.
5. Team & Collaboration
A successful Bill of Materials process requires collaboration between multiple members of the team. That’s why it is important to have collaborative tools to support the BOM management process.
You will need to stay connected with multiple engineers, production planners, procurement, contractors, and suppliers. Without successful collaboration, you won’t be able to define a correct Bill of Materials, which will lead to mistakes, additional costs, and delays.
6. Analysis & Calculation
Bill of Materials is a data foundation for your product. You need to have the ability to perform various analytics and calculations based on the BOM data. The most typical one is cost rollup.
Predicting the cost is one of the most critical elements in the product development process. A correct and complete BOM is a foundation for cost rollup. Beyond that, BOM can be used for many other tasks: suppliers’ selection, lead time validation, contract manufacturing, and others.
Product Lifecycle Management – OpenBOM
If you have questions or would like to know more about the bill of materials, OpenBOM support can help you, just get in touch! We also offer complete services to support your product lifecycle management from prototype to production and maintenance.
Explore our BOM Management Solutions to find the right fit for your needs. Ready to get started? Sign up for a 14-day free trial today and streamline your BOM processes with ease.
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.