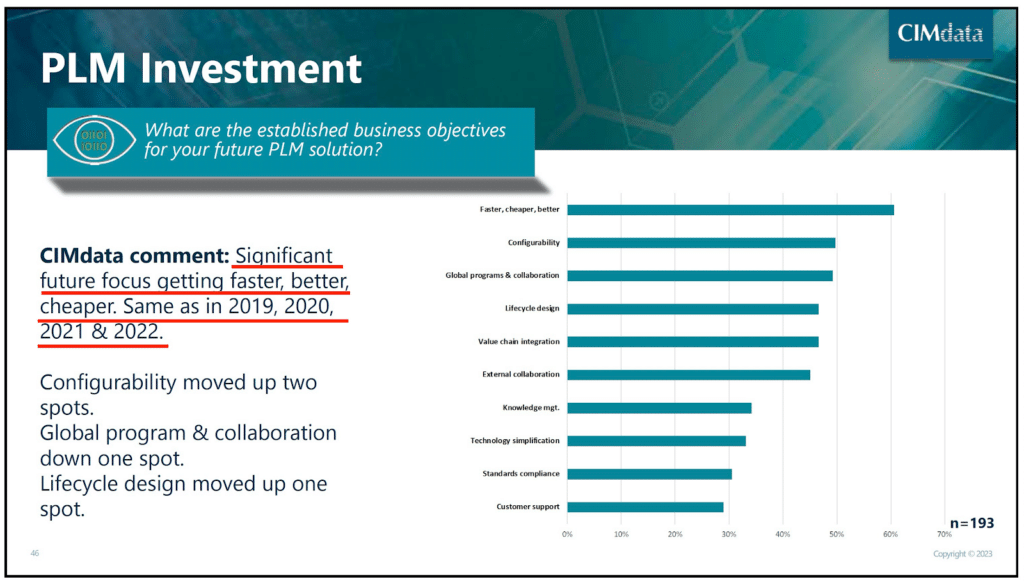
The reality of modern product development and manufacturing is scary. Product complexity is skyrocketing these days. Products are complex systems combining mechanical, electrical, electronic, and software components. How can manufacturing companies deal with such a high level of complexity and, at the same time, be competitive and deliver new products with an increased speed and level of innovation? The industrial companies speak loud and clear about what they want from PLM vendors. The business objective for tools is to focus on “faster, better, and cheaper” is at the top of the priority list. Here is a slide from CIMdata PLM Industry Forum I attended last month.
While a digital transformation is a generic answer to all these challenges, the question of what will bring differentiation to modern PLM? , is still not answered. PLM mindshare vendors are in the process of turning their platforms into SaaS by hosting existing products using PaaS solutions (AWS, Azure, GCP). It will certainly solve painful problems of software configurations and upgrade, but how it will help to deliver future PLM solution demand to develop better, faster, and cheaper?
Embracing Complexity of Networks
In our increasingly interconnected world, complexity is all around us. From the challenges we face in our personal lives to the complex systems and processes that govern our societies, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed and uncertain about how to navigate the intricacies of modern life. As such, product development and manufacturing are extremely complex.
The opportunity to embrace complexity can also be an opportunity for growth, innovation, and creativity. By acknowledging the interdependent and dynamic nature of product development, manufacturing, and supply chain we can approach problems with greater nuance and flexibility, seeking out new perspectives and solutions that may have been overlooked in a more simplistic or linear approach. By recognizing and embracing complexity, we can cultivate a more nuanced and holistic understanding of the world, and harness its potential to create meaningful change in our lives and communities.
While “PLM holy grail” was defined as a process of managing a product’s lifecycle from inception, through design and manufacturing, to sales, service, and eventually retirement, such a vision was never realized in practice. In fact, all established PLM solutions are basically SQL databases designed for a single company to manage CAD files and product change records. The same CIMdata State of PLM 2023 review clearly shows that most PLM implementations are still focusing on core functions of data management and engineering release functions.
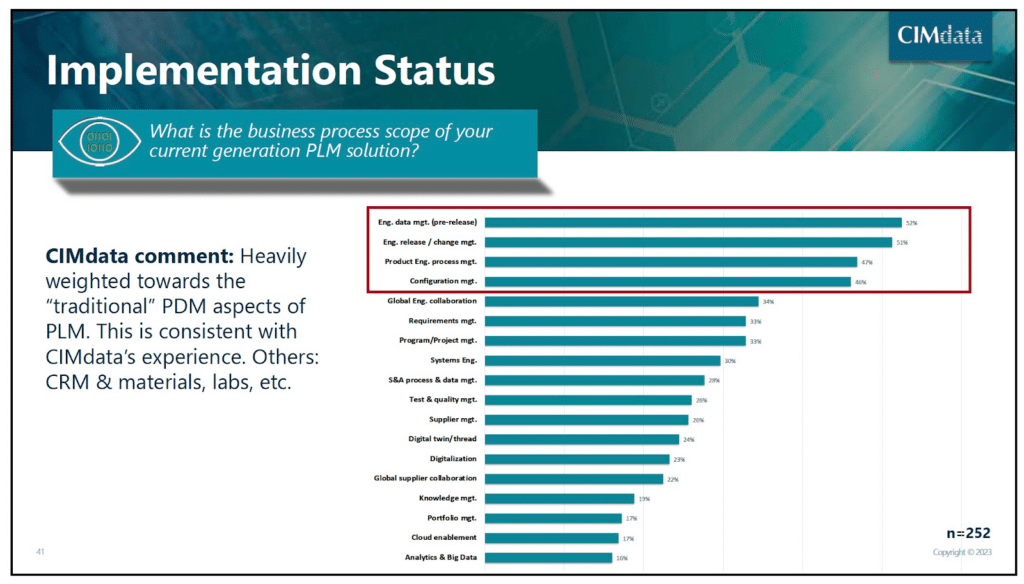
Here is a big disconnect between PLM vision, manufacturing reality and existing PLM systems. The reality of product development and manufacturing can be represented as a network where multiple companies are operating in the interconnected world forming manufacturing networks. At the same time, product lifecycle management (PLM) platforms are old-fashion applications using relational databases to store data. The limitations of these PLM systems are well known and their capabilities to address the globally networked world are limited. Read more here – What is wrong with traditional PLM systems?
To overcome the complexity of modern product lifecycle management and manufacturing, the industry must switch to a new model – networked data structures, graph databases, and network-based platforms.
At OpenBOM, we embraced network platform principles allowing companies to connect together, collaborate, and share information. Check some of OpenBOM’s earlier articles to learn about OpenBOM’s multi-tenant architecture and Digital Thread Services to support collaboration with contractors and suppliers.
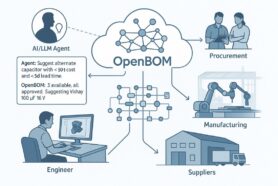
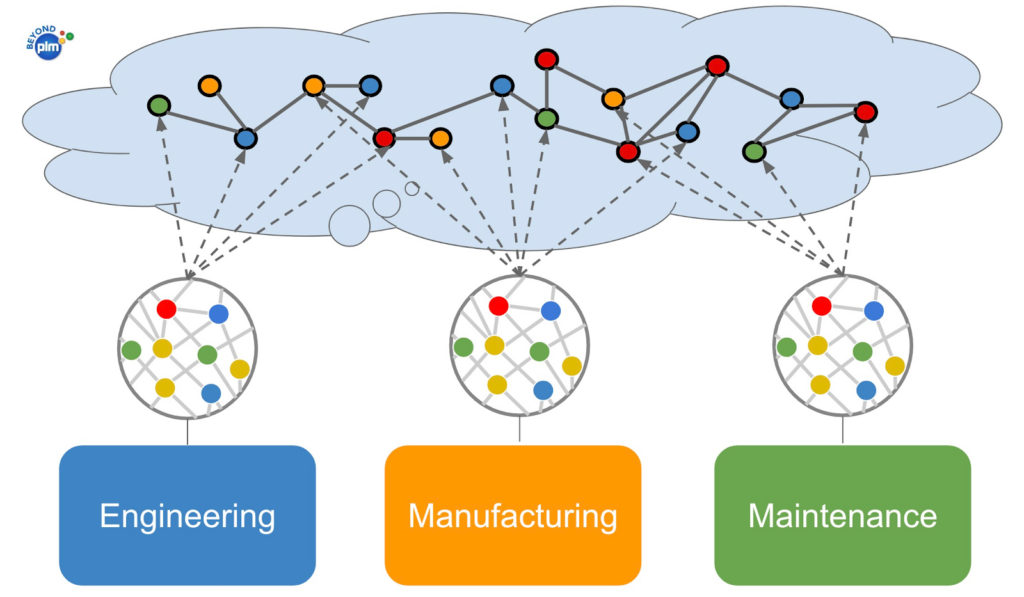
One of the most important elements of OpenBOM architecture is its graph database core allowing management of product complexity and building Product Knowledge Graphs and advanced semantic relationships using data integrations with multiple engineering systems.
Why Graph Data Layer?
As the world becomes more interconnected and businesses strive to create innovative products, the complexity of product development continues to increase. In order to effectively manage this complexity, businesses are turning to graph models to help them better understand their products, customers, and markets. Let’s explore how the graph data layer will help to organize data.
A graph model is a mathematical structure that is used to represent relationships between objects. In a graph, objects are represented as nodes, and the relationships between those objects are represented as edges. Graphs can be used to model a wide range of phenomena, from social networks to chemical reactions.
In product development, a graph model can be used to represent the relationships between different components of a product. For example, a graph model could be used to represent the different parts of a car and how they are connected. By representing a product in this way, businesses can better understand the relationships between different components and how changes to one component can affect the entire product. OpenBOM is using graph database technology to build graph data layer.
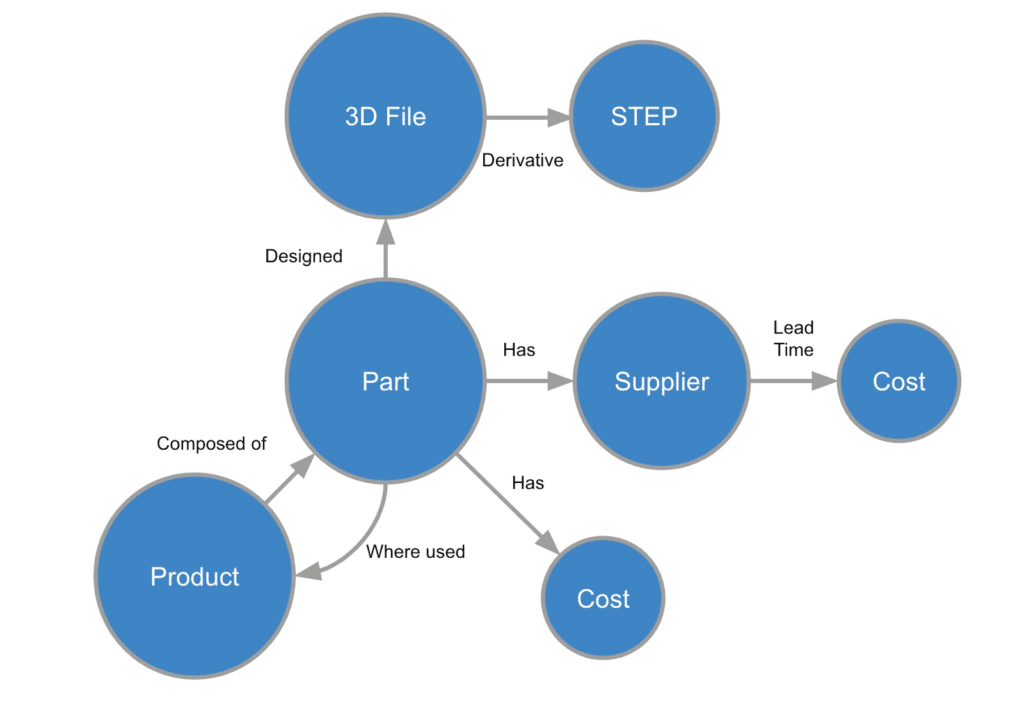
As products become more complex, it becomes increasingly difficult to understand how different components interact with each other. By representing a product as a graph, businesses can more easily visualize the relationships between different components and identify areas where changes need to be made. Another advantage of using a graph model is that it allows businesses to better understand their customers. By representing customer interactions as a graph, businesses can identify patterns in customer behavior and use this information to create more targeted products and marketing campaigns. In addition, a graph model can be used to represent the relationships between different markets. By modeling the relationships between different markets as a graph, businesses can identify opportunities for growth and expansion.
Check my article speaking about the importance of Knowledge Graphs for PLM architecture.
A graph data layer is an essential tool for businesses looking to embrace product development complexity. By representing products, customers, and markets as graphs, businesses can more effectively manage complexity and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
Now, let’s come back to the topic of digital transformation as a way to answer customers’ demand for “better, faster, cheaper” solutions.
Digital Transformation = Data+Cloud+AI
For the last decade, we are all realized a dangerous divide between companies that have AI (Artificial Intelligence) and other companies that didn’t embrace these capabilities. I’m sure you can see it in your everyday life. How is it possible that Google recognizes my face and my driving routes, can understand my speech, and apparently knows that I like a specific restaurant and desire a specific type of vacation? At the same time, it takes manufacturing companies months to add a few new additional attributes to the last supply chain report.
The answer to this question is that digital organizations like Google for years accepted the reality of data complexity, didn’t look for a quick fix, and built technologies and solutions by placing graph models and networks in their complex systems. The good news is that many of the elements of these solutions are becoming available today. This is why OpenBOM is adopting these new models and tech to deliver a different solution for manufacturing enterprises.
The answer to what real digital transformation is lies in the combination of three key elements – (1) data; (2) cloud ; (3) artificial intelligence. All of them are using network architecture and result in a powerful solution that can address the complexity of product lifecycle management for the 21st century.
Data Network represents an information model with all dependencies, and semantic relationships describing product lifecycle management. The foundation of the data network is product information (Digital Web) – a knowledge graph that “knows” everything about the product – assembly, components, suppliers, machines, cost, requirements, maintenance, etc.
Cloud is a computing and data storage network allowing unlimited capabilities to manage information, and providing computational resources to scale. Cloud combined with data as a service provides a way to break through the limitations of a single SQL database (legacy PLM) to deliver future computing capabilities
AI (Neural Network) is a capability of a system to perform tasks that usually require human interaction. A recent breakthrough in GAI methods can solidify the vision in the future PLM AI advancement – GPT, Hybrid LLM, and Copilots. Read more about BOM copilot research.
What is my conclusion?
Network model and graph database is a foundation of OpenBOM solution to model a complex product data model – knowledge graphs to support the complexity of modern product development. This is where the real digital thread begins and the potential of the digital web of product lifecycle management can be realized. Network architecture replaces the limited relational model, supports complex relationships, and complex queries, and improves query performance. Graph databases outperform relational databases in the ability to manage multiple data points and complex data elements in a flexible way. Knowledge graphs are a foundation of OpenBOM AI ( I will talk about it in future articles).
In the meantime, the data management pain is real and many companies are looking at how to simplify their data management and streamline collaboration beyond Excel and emails.
REGISTER FOR FREE to check how OpenBOM can help you today.
Best, Oleg
Join our newsletter to receive a weekly portion of news, articles, and tips about OpenBOM and our community.